In this world wide world, data moving from one point to another brings latency. While this may seem insignificant from the perspective of normal life, it makes a big difference in the operation of the Internet.
What is Network Latency?
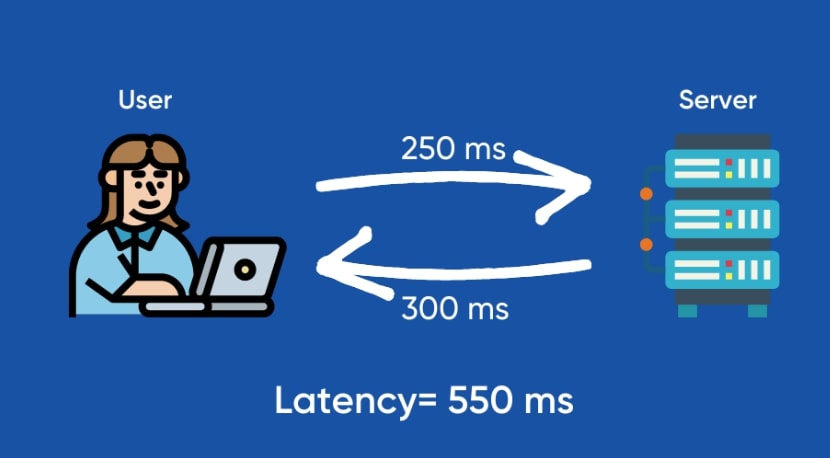
Simply put, Network Latency is the round trip time it takes for a signal to leave the user to travel to the server and back. But it’s not as simple as it looks in the chart above. What it misses is the junction where the signal bounces between two endpoints. This routing is the main cause of Network Latency.
Be aware that latency is almost twice as long as ping, which is the time it takes for data to move from the user to the server. Still, some people use latency and ping interchangeably, which is conceptually wrong. And, although some people are confused, latency is different from throughput and bandwidth.
Zero latency is the goal for all of us. But distance and intermediate connections cause unavoidable latency. Nevertheless, network administrators minimize latency for various Internet applications, such as gaming, video calls, etc.
Causes of Network Latency
The number one culprit for high latency is distance. Greater distance between the starting point and the server means more intermediate junctions. Each of these junctions has its own bottleneck, adding a small amount of latency to the overall latency.
Another major reason could be that the website is not optimized. This can be caused by several issues such as the presence of large media files, tracking cookies (from services like Google Analytics), poor web hosting services, etc. It is also possible that the user’s hardware is inefficient (e.g. low memory), resulting in high latency. Finally, each element of the network, such as cables, routers, servers, client hardware, software, etc., adds some lag.
Measuring Network Latency
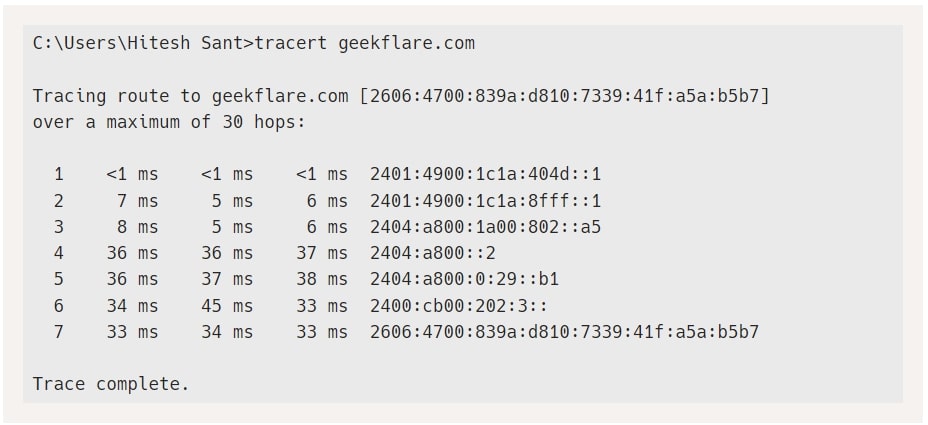
This is the most common method and can be measured directly from your computer. Open a command prompt and enter tracert and the destination address.
Nirsoft Latency View
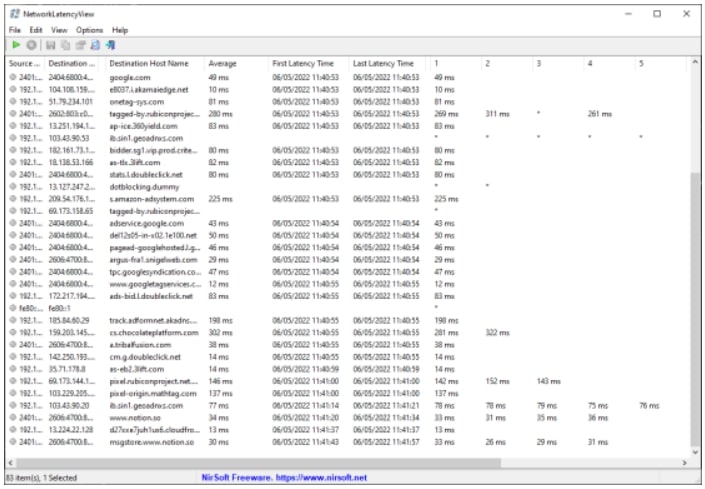
While traceroute is handy for single endpoints with less than 30 hops, Nirsoft Latency View reveals the lag for all outbound connections. In addition, this completely free tool provides you with average latency values for all connections to the same destination.
SolarWinds Traceroute NG
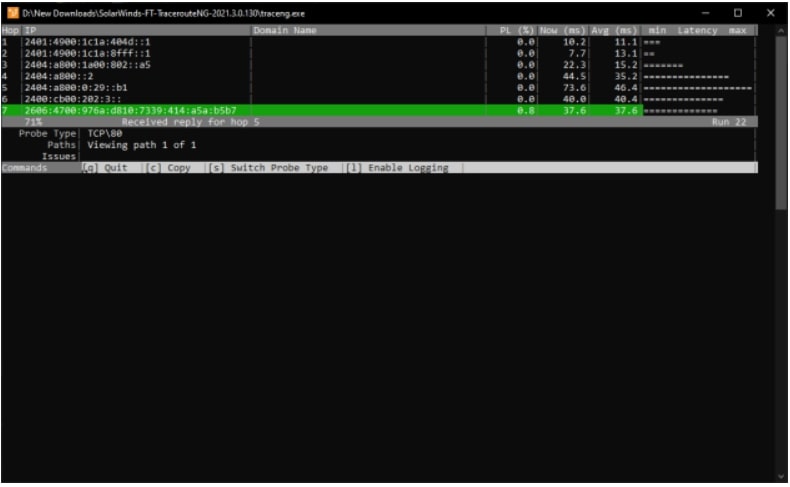
Traceroute NG is another great tool for running multiple latency tests against a single server. This will keep checking latency values until you stop. The dashboard provides you with immediate and average latency values for a specific destination. Again, there are many tools to find out the network path and latency.
The Impact of High Latency
You may be wondering why lag is so important. It’s not just gamers, our complete Internet experience depends on it. High latency values can make each Internet connection slow loading services until the user switches to a computer. For example, if Facebook took 30 seconds to load every time, would you use it? Statistics show that every extra second a site takes to load translates into a high bounce rate, and even a two-second load time can result in nearly 10% fewer users.
Increase this to 7 seconds and you will see a 32% drop in network traffic. It’s not just visitors; high lag values can affect anything you do online, whether it’s a video call, a presentation, a payment, etc. Even if the network capacity (aka bandwidth) is large, this will reduce the data transfer capacity (aka throughput) per unit time. The conclusion is that only networks with low latency are useful, and network administrators are constantly trying to bring them down to improve productivity.
Reducing Network Latency
While you can’t update or improve all networks between endpoints, there are a few things to keep in mind. The mechanics of optimizing your network start with targeting its biggest enemy — distance. The best practice is to host your business where you have the majority of your customers.
However, if you have a global clientele, then choosing a content delivery network (CDN) may solve the problem. Note that while there are free CDNs on the market, using them can have a negative impact on your web property. Therefore, if you use one, it is a good idea to perform a site audit to verify these changes.
Regular software updates can be the next step in improving high Network Latency. In addition, ensure that your hardware has sufficient capacity to utilize the full network potential.
In addition, wireless networks typically have much greater lag. Therefore, use a wired connection whenever possible. In addition, choosing a top-notch fiber optic network will further help reduce lag.
In addition, using HTTP/2 reduces latency by loading various page elements simultaneously, etc. You can check this with Geekflare’s HTTP/2 test. Finally, try implementing data caching and optimizing the media to minimize latency.